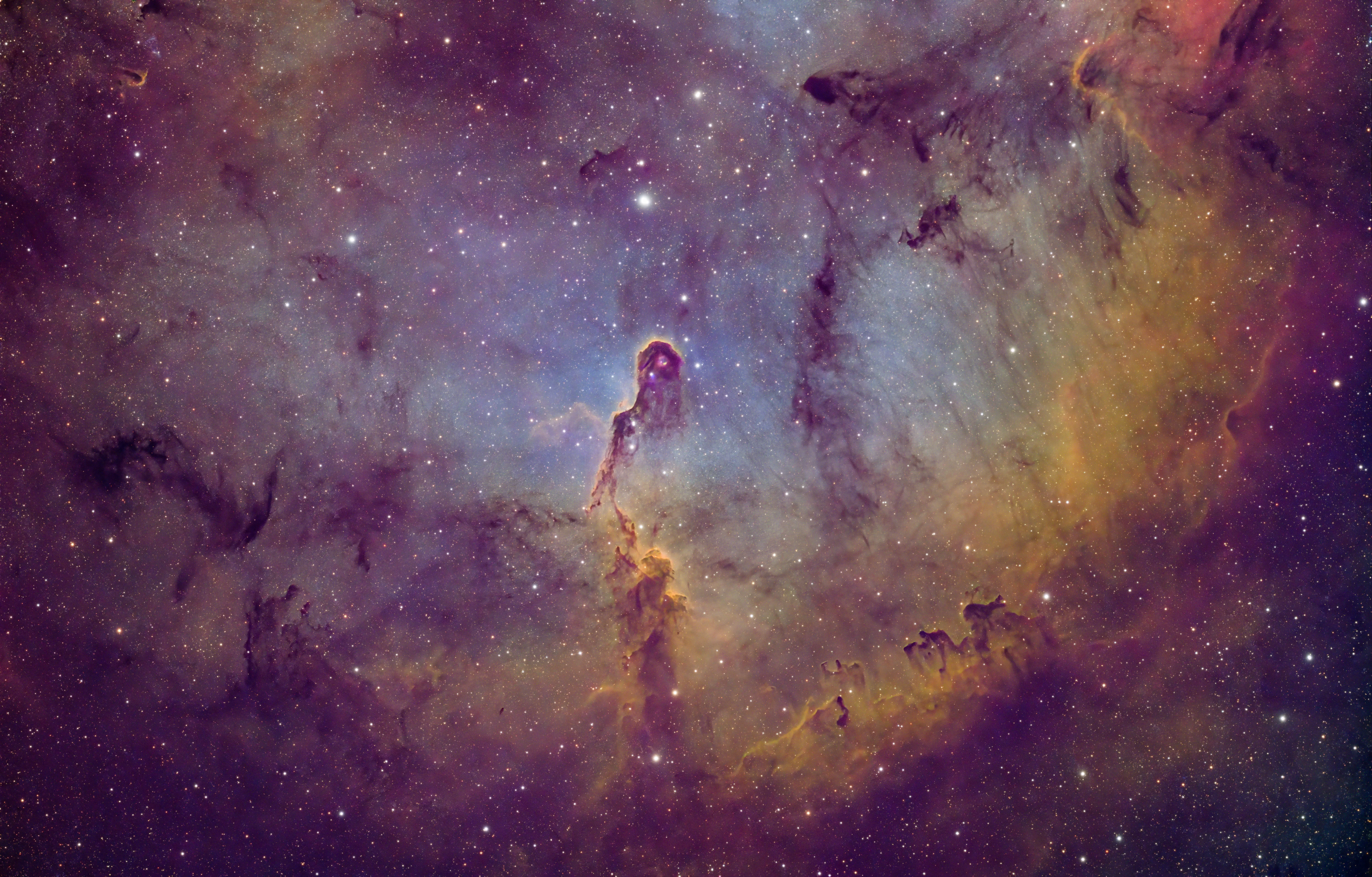
The Orion Complex astrophoto taken with the Redcat 51
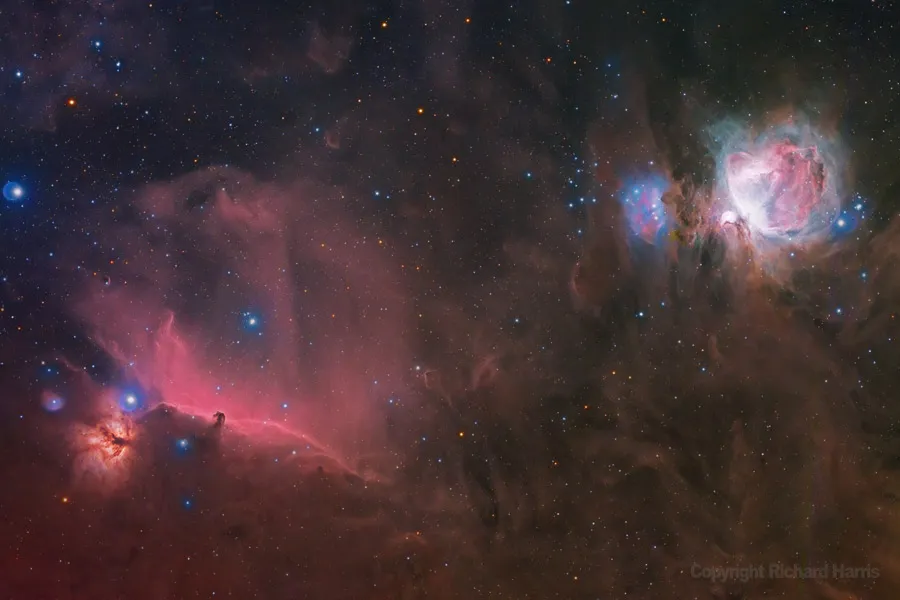

Astrophoto of the Orion Complex taken using the Redcat 51 telescope and the ZWO ASI6200MM in mono. LRGB+SHO data combined with just over 4 hours of acquisition time.
The Orion Molecular Cloud Complex, often simply referred to as the Orion Complex, is a star-forming region located in the constellation Orion, it's been on my bucket list for a long time. It's an awe-inspiring stellar nursery where new stars are born from the vast clouds of gas and dust. One of the most exciting features within the Orion Complex is the famous Orion Nebula (Messier 42), a stunning emission nebula that is visible to the naked eye as a fuzzy patch in Orion's sword. This nebula is a hotbed of stellar activity, with young, massive stars illuminating the surrounding gas and causing it to glow with vibrant colors. The Orion Nebula is one of the closest stellar nurseries to Earth and offers a spectacular view of the processes that shape the birth of stars, making it a favorite target for amateur and professional astronomers alike.
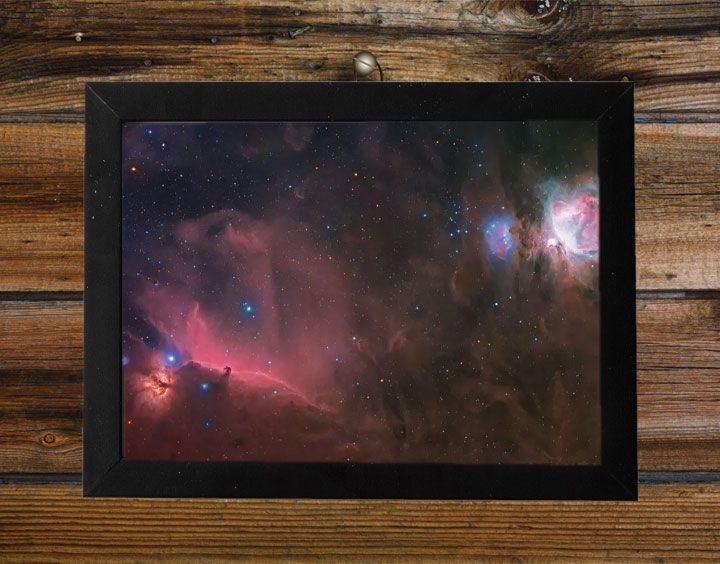

The Complete region in it's entirety is one of the most active regions in the night sky. You can actually see some of it just using your nake eye. It takes special equipment and processing to bring out the details.
The Complex is home to five main components — Orion A and B, which are two giant molecular clouds, Orion OB1 Association, Lambda Orionis Molecular Ring, which is centered on Meissa, and the Orion-Eridanus Superbubble.
The Complex is in our own Milkyway galaxy -about 1200 light years away.
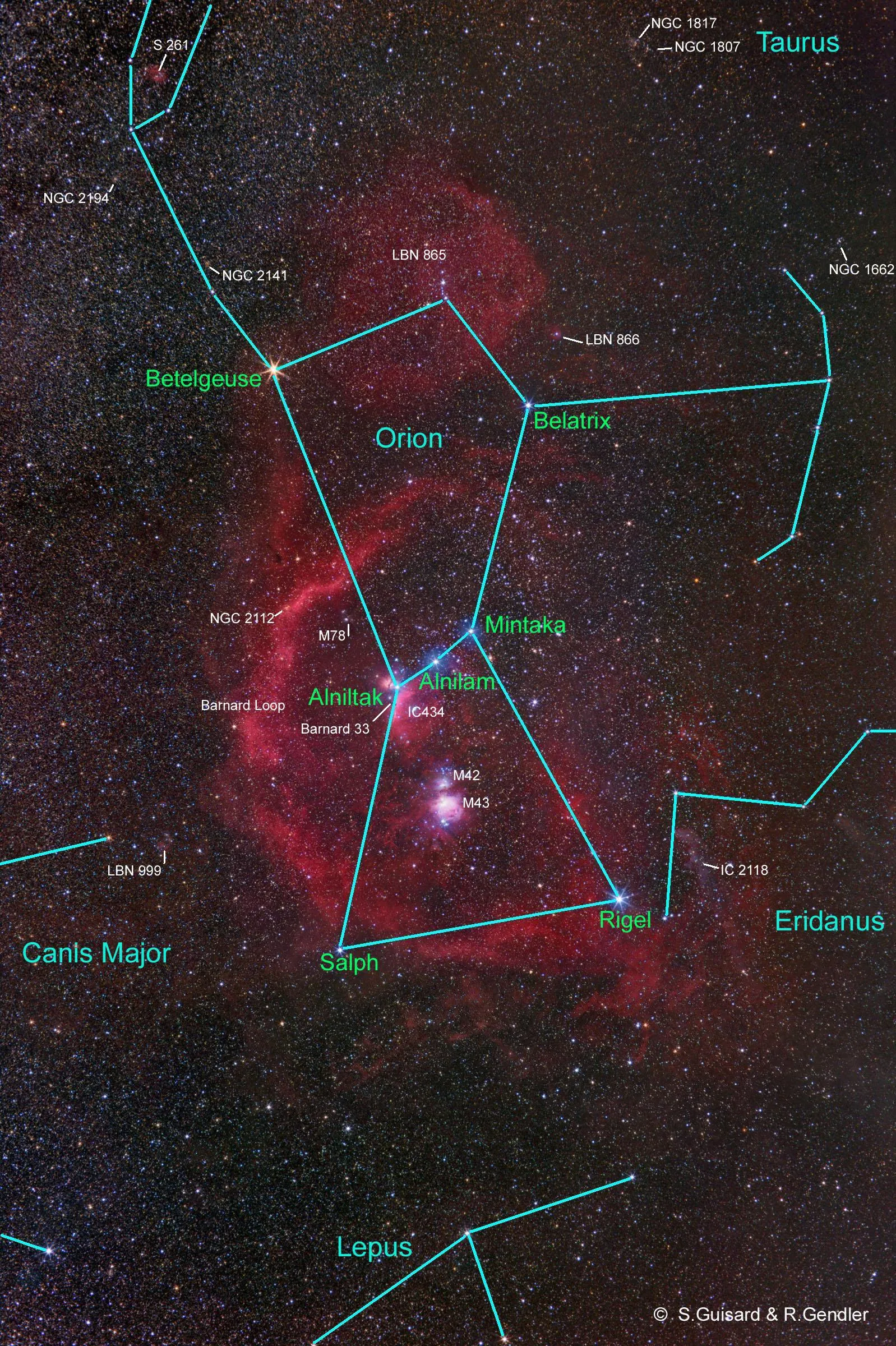
The Complex star map above gives some hint as to the size and total objects in the region.
There are two of the most recognized deep space objects inside the complex, the Orion Nebula, and the Horsehead Nebula.
The Orion Nebula
- Brightness and Visibility: The nebula is one of the brightest nebulae visible to the naked eye from Earth. Its glow is prominent even in areas with some light pollution, making it easily noticeable.
- Proximity: The Orion Nebula is relatively close to Earth, located at a distance of about 1,344 light-years. This proximity allows it to appear larger and more detailed in the night sky.
- Position in Orion's Belt: The Orion Nebula is situated in the "sword" portion of the Orion constellation, just below the three stars that form Orion's Belt. This makes it a recognizable part of a familiar constellation.
- Naked-Eye and Binocular Visibility: While a telescope reveals more intricate details, the Orion Nebula is also visible to the naked eye as a faint smudge in the sword of Orion's constellation. This means that even casual stargazers can spot it.
- Star-Forming Activity: The nebula's distinct appearance is due to its ongoing star-forming activity. The young, hot stars within the nebula emit ultraviolet radiation that excites the surrounding gas, causing it to glow in various colors.
- Cultural Significance: The Orion constellation and its nebula have been recognized and named in various cultures throughout history. The nebula's location near Orion's Belt and its unique appearance have contributed to its significance in different mythologies and stories.
The Horsehead Nebula
- Distinctive Shape: The Horsehead Nebula's silhouette resembles a horse's head, which is a unique and easily recognizable shape in the night sky. This distinctive form captures people's imagination and makes it a favorite target for astrophotography and observation.
- Dark Nebula: The Horsehead Nebula is a dark nebula, meaning it's a cloud of gas and dust that blocks the light from background stars and nebulae. This contrast between the dark nebula and the bright emission nebulae around it creates a visually striking scene.
- Challenging Observation: Spotting the Horsehead Nebula requires good visibility and a telescope, making it a challenge for amateur astronomers. This challenge adds to its allure and makes successfully observing it a rewarding accomplishment.
- Astrophotography Subject: Photographing the Horsehead Nebula with long-exposure techniques reveals its intricate details, creating stunning and captivating images. Its intricate tendrils of dark dust against the backdrop of colorful emission nebulae make for visually striking astrophotography subjects.
- Location: The Horsehead Nebula is located near the star Alnitak, which is one of the three stars in Orion's Belt. Its proximity to a well-known and easily identifiable constellation makes it easier for observers to locate.
- Cultural and Mythological Associations: The nebula's unique shape has led to various cultural and mythological interpretations in different societies. These associations add layers of depth and meaning to its popularity.
The great Orion complex region details.
Subjects: M42, M43, Horsehead Nebula, N2024 (Flame Nebula), M78
Photo taken November 26th, 2022
Location: Strafford, Mo
Latitude: 37.27 N, Longitude: 93.12 W
Equipment: Williams Optics Redcat 51
Mount: AM5 Harmonic drive
Camera: ASI 6200MM with RGB+L data, Sulfur II, Oxygen III, and Ha data combined and processed using PixInsight, final adjustments made in Adobe Photoshop
Total acquisition time of 4 hours, accumulated over 5 minute sub exposures across all filters noted
Photographers notes: The Orion region has always been a beautiful target for me with such rich colors across many wavelengths. To be able to capture so many objects in one frame was a goal I had for many years.
Copyright Richard Harris
About the Author

Meet Richard Harris, a passionate and dedicated astronomer who embarked on a cosmic journey at the age of 11 and has been reaching for the stars ever since. Born with an innate curiosity for the universe. Richard's fascination with astronomy ignited when he first gazed up at the night sky and felt an indescribable connection to the cosmos and creation. As a younger lad, Richard spent countless hours poring over astronomy books, studying constellations, and learning about the celestial wonders that grace our skies. In 2001, Richard invented the HyperTune telescope process, which has grown into the standard for German equatorial telescope mount tuning across the globe. He is also the founder of ScopeTrader, a global resource helping to grow the hobby of astronomy which started in 2002, and the CEO of Moonbeam software company, started in 2008. When he's not taking photos of our universe, you can find him with family, playing guitar, or traveling.











